Fitter First Year Tools Figure
Flat Drill Fig 1
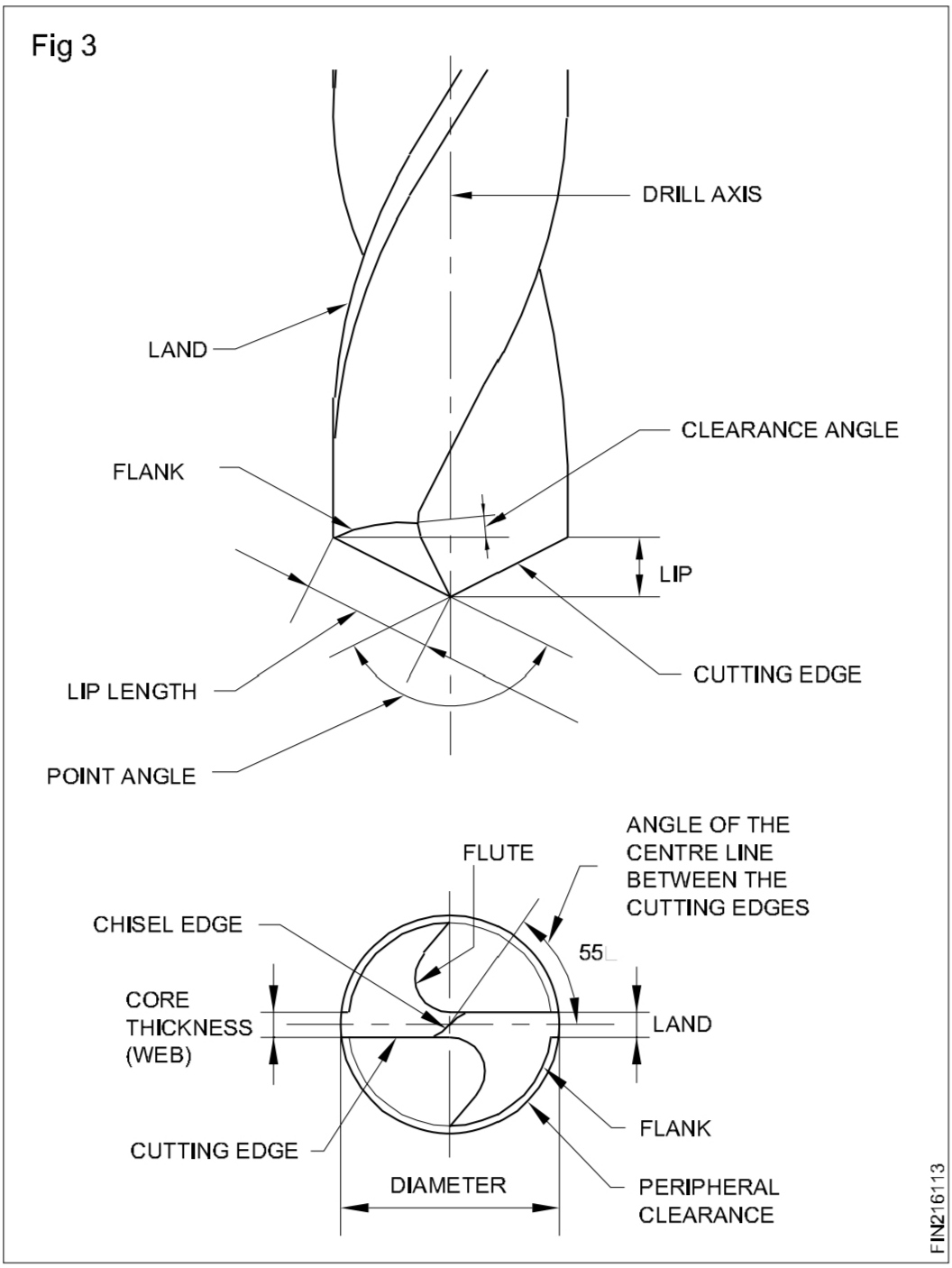 |
| Parts of twist Drill |
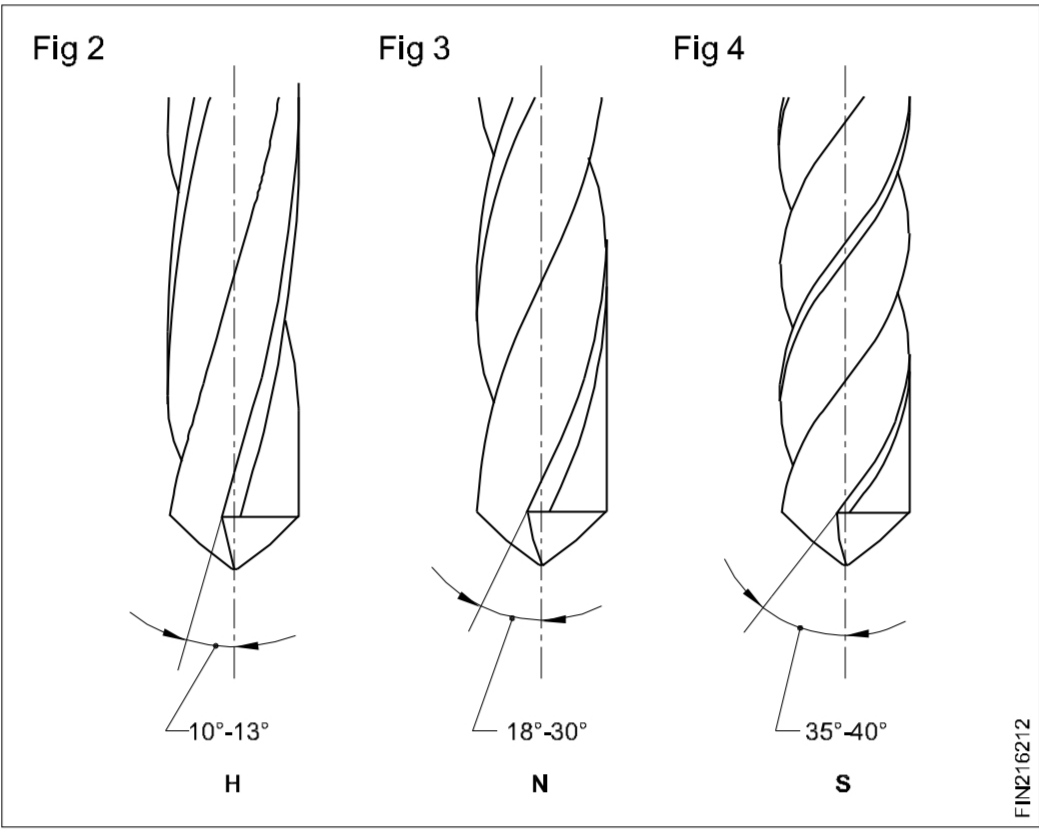 |
| Helix Angle H, N, S |
 |
| Lip Clearance Angle |
Chisel Edge Angle/Web Angle Fig 5
 |
| Web Angle |
 |
| Drills for different material |
Recommend Cutting Speeds
Drill Chuck Fig 1
Taper Slive And Socket Fig 2
Use a drift to remove drills and sockets from the machine spindle. Fig 3
 |
| Drift |
To provide a recess for the head of a countersink screw, so that it is flush with the surface after fixing Fig 1
 |
| Counter Shinking |
The commonly used countersinks have multiple cutting edges and are available in taper shank and straight shank. Fig 2
 |
| Counter Shinking |
Countersinks with Pilot Fig 3
 |
| Counter Shinks with Pilot |
Counter Boring Fig 1
Counter Boring with Pilot Fig 2
Reaming enlarging by finishing previously drilled holes Fig 1
Hand Reamer Fig 2B
Flutes Fig 4
 |
| Rake Angle |
Clearance Angle Fig 6
Hand reamer with pilot Fig 4b
Socket reamer with parallel shank (Figs 5a and 5b)
Taper pin hand reamer (Fig 5c)
straight and helical fluted reamers Fig 6
Tags:
FITTER TOOLS



















